Degenerative disc disease (DDD) is a common condition that occurs as a natural part of the aging process. It is not truly a disease but rather a progressive deterioration of the discs that act as cushions between the vertebrae of the spine.
Degenerative Disc Disease
Overview
What is a Spinal Disc?
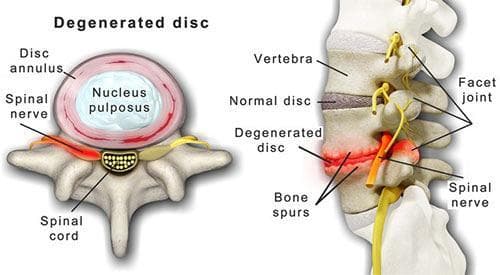
Each spinal disc is made of two parts: a tough, fibrous outer layer called the annulus fibrosus and a soft, jelly-like inner core known as the nucleus pulposus. These discs function as shock absorbers and allow the spine to bend, twist, and move with daily activities.
Causes and Progression
As we age, the discs lose their water and protein content, becoming less flexible and thinner. Over time, this wear and tear can lead to a variety of spinal issues, including: disc herniations, instability, loss of shock absorption, stiffness, disc bulging, nerve compression, or bone spurs. Certain habits can progress the disease such as smoking, using poor lifting mechanics, repetitive bending or vibratory stresses, and being overweight.
Symptoms
Many people have some degree of disc degeneration but experience no pain. However, on occasion symptoms can develop and may include:
- Chronic back or neck pain: Disc pain is often described as a dull ache and may be worse when sitting or with certain activities like bending, lifting, or twisting. Pain from DDD often occurs in flare-ups, lasting for days or months before subsiding.
- Pain and numbness: Nerve compression can cause pain, tingling, or numbness to travel down the arms (neck DDD) or legs (back DDD).
- Weakness: In rare cases, severe nerve compression can lead to muscle weakness in the arms or legs.
Non-Surgical Treatments
- Physical Therapy and Exercise: Strengthening core and back muscles to improve stability as well as regular stretching exercises to improve lumbar and hamstring flexibility.
- Lifestyle modifications: Maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding activities that aggravate the pain.
- Medications: Over-the-counter anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen or naproxen are the preferred first-line medication to manage pain symptoms. Stronger prescription medication may be considered if these fail.
- Injections: Occasionally steroid injections can provide temporary relief by reducing inflammation around the disc and nerves.
Surgical Treatment
Surgery is considered as a last resort when non-surgical options have failed and the patient is experiencing severe, debilitating pain or concerning neurologic deficits.